Advertisement
Electrical Imbalance and Chemical Bonds
Appears in
By Harold McGee
Published 2004
Electron hunger is also the basis for the chemical bond, an interaction between atoms or molecules that holds them together, either loosely or tightly, momentarily or indefinitely. There are several different kinds of chemical bonds that are important in the kitchen, as they are throughout nature.
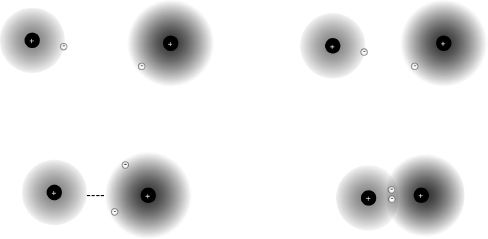
Ionic and covalent bonds. Left: An ionic bond results when an atom completely captures one or more electrons of another atom, and the two atoms experience an attractive force (dotted line) due to their opposite electrical charges. Right: In the covalent bond, atoms share electrons, and thereby form stable combinations called molecules.


