Advertisement
Saturated and Unsaturated Fats, Hydrogenation, and Trans Fatty Acids
Appears in
By Harold McGee
Published 2004
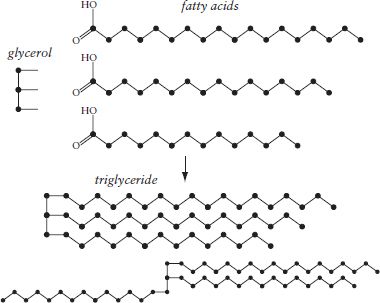
Fats and fatty acids. Fatty acids are mainly chains of carbon atoms, shown here as black dots. (Each carbon atom has two hydrogen atoms projecting from it; the hydrogen atoms are not shown.) A fat molecule is a triglyceride, which is formed from one molecule of glycerol and three fatty acids. The acidic heads of the fatty acids are capped and neutralized by the glycerol, so the triglyceride as a whole no longer has a polar, water-compatible end. The fatty-acid chains can rotate around the glycerol head to form chair-like arrangements (bottom).


